The LED lighting industry continues to adopt the concept of dimming in LED lighting fixtures. Hence dimmable LED drivers constantly get industrial attention.
As we know, dimming fulfills visual needs and saves energy in LED lighting fixtures. As a result, when we analyze the concept of dimming, we cannot neglect the subject: dimming curve.
Dimming curves are parameters or function images that specify the response of dimmers voltage output to control signal input.
The dimming curve shows how electrical parameters of LED drivers respond to control signal input. As the LED driver translates the signal to currents that power the dimmable LED, we can alternate with the different brightness levels of the LED light.
Concepts You Should Understand Before Choosing Dimming Curve
When we talk about “dimming,” we should ask ourselves, what is the goal behind this concept?

Dimming exists to fulfill the following targets;
- Environmental and Visual needs: this involves the level of brightness appealing to the human eye
- Save energy: the dimming feature of lighting fixtures can reduce power consumption, hence saving cost.
- Expand the life time: less output means less power loss and temperature of electrolytic capacitors, thus by dimming control LED drivers life time is lengthened.
Then the dimming curve plays a massive role in helping the LED lighting fixtures achieve the above goals.
With all this at heart, it is now clear that you choose dimming curves that will help the light fixtures meet the goal of a dimmable LED driver.
The LED Dimming System
The LED dimming system should be your first stop. It consists of a LED driver, dimmer(controller), and luminaire.
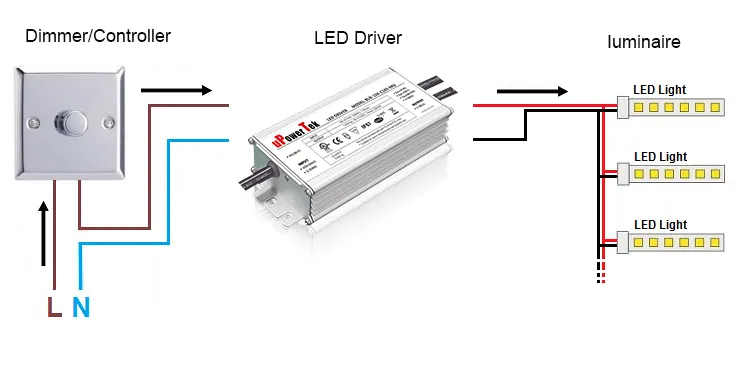
When you configure this system correctly, there will be quality dimming performance. The system works with a model we can summarize in three phases below;
- Trigger the slider movement in the dimmer
- Dimmer send signals to the LED driver
- The LED driver triggers electric currents that power the LED
The above processes form a response which we can see as the dimming curves.
Types of Dimming Curves
There are several dimming curves, and some LED drivers enable users to switch between the different dimming curves.
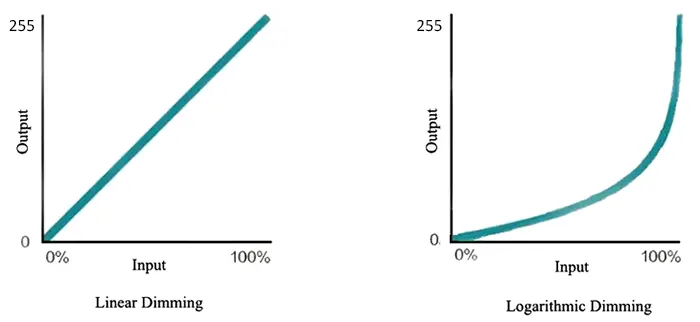
The dimming curves adopt standard mathematical models such as square, sine, cosine, cube, etc. Therefore, due analysis on a dimming curve such as modifying, superimposing, or shifting can upgrade the performance of LED drivers.
Let’s have an in-depth analysis of the dimming curves relevant to the LED lighting industry.
Linear Dimming Curves
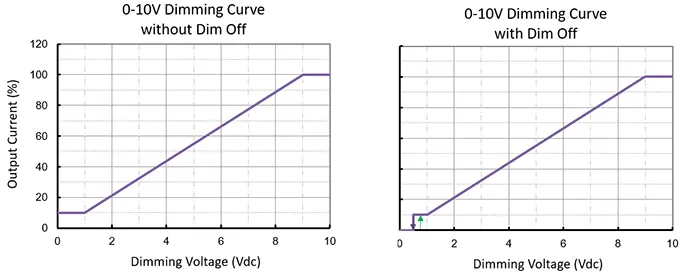
One thing is constant in linear dimming curves, and we call it “direct proportionality.” It means that in a linear dimming curve, the brightness output(voltage output) is linear(directly proportional) to the signal input. And 0-10V dimming regulated in IEC60929 Annex E is often behaving like linear dimming though it does not have to be.
Let’s make this a bit practical. If there is a 30% signal input, the brightness output will also be 30% as the curves below shows which are always apprearing in product datasheets.
Logarithmic Dimming Curve
The logarithmic dimming curve is miles different from the linear curve. The logarithmic dimming curve is when the signal value slowly changes at deeper dimming levels and changes faster at the brighter parts.
Typically, the logarithmic dimming curve features in commercial light applications, especially DALI applications though DALI can also support linear dimming curve. IEC 62386 defines the dimming range of a DALI LED driver from 0.1 to 100 % by 255 steps.
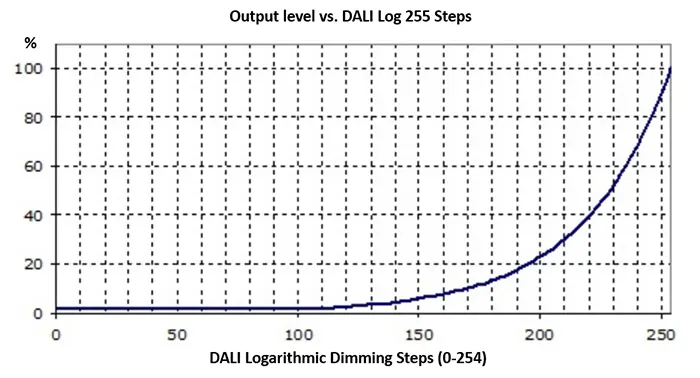
A logarithmic dimming curve typically results in natural changes of brightness and the reason is shown as below.
Measured and Perceived Light
This concept is straightforward.
- Measured light is the amount of light we see on the measuring equipment(the light meter)
- Perceived light is the amount of light your eyes see and interpret.
The measured and perceived light is crucial to configure a quality dimming model properly. It is one of the yardsticks to judge a dimming effect.
See how they relate to the dimming curve below.
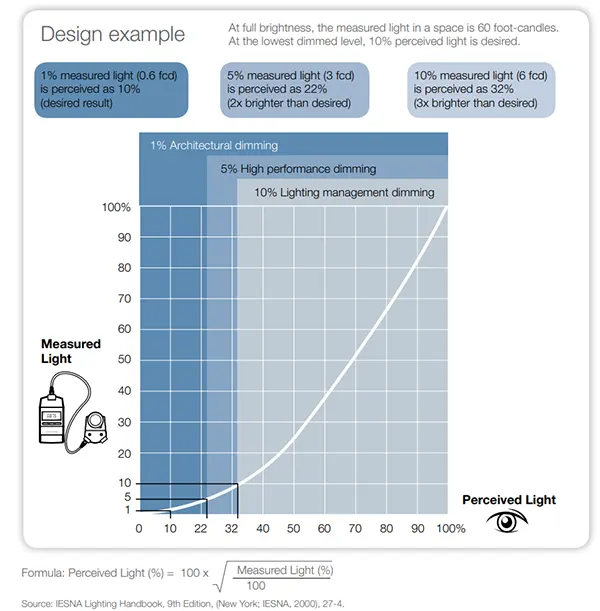
From the image above, the dimming curve indicates a response of a dimming system with 10% measured light and 32% perceived light. This implies that the brightness of the LED does not match what our eyes see so a more precise and slower dimming is absolutely necessary for the application which needs low level brightness, especially like hotel, conference room,architecture and etc.
Final Thoughts: Let uPowerTek Give You the Right Dimming Curve
Following the article, you will see how important it is to use the right dimming curve for every LED lighting model.
The great news is that you can leave all the stress on uPowerTek, as we will help you with the best dimming curve choices.
It’s time to unravel the perfect dimming experience.





